[Algorithm] 탐욕 알고리즘 (Greedy Algorithm)
Greedy Algorithm (탐욕 알고리즘)
- 최상의 옵션을 선택하는 알고리즘
- 솔루션을 하나씩 구축하는 알고리즘 패러다임
- 최상의 출력을 제공 할 수도 있고 제공하지 않을 수도 있음
연산
- 선택을 해야하는 특정 순간 가장 좋은 방법 / 옵션을 찾아 선택하는 알고리즘
종류
- Huffman code (허프만 코드)
- Travelling Salesman Problem (외판원 문제)
- Prim’s Minimal Spanning Tree Algorithm (프림의 최소 신장트리 문제)
- Kruskal’s Minimal Spanning Tree Algorithm (크루스칼의 최소 신장트리 문제)
- Dijkstra’s Minimal Spanning Tree Algorithm (다익스트라의 최소 신장트리 문제)
- Graph - Map Coloring
- Graph - Vertex Cover
- Job Scheduling Problem
- Machine scheduling
- Fractional Knapsack Problem (부분 배낭 문제)
- Activity Selection Problem (활동 선택 문제)
자바를 이용하여 탐욕알고리즘 - 동전선택문제(=거스름돈) 구현
- 가치가 높은 동전을 선택
- 동전을 더하여 총 금액을 초과하지 않을 만큼 각 동전의 필요 갯수 구하기
public static int[][] countCoin(int amount, int[] arr) {
int[] cointCount = new int[arr.length];
int[][] result = new int[arr.length][2];
int total = amount;
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length ; i++) {
if (total >= 0){
//coin의 갯수가 들어감
cointCount[i] = total/arr[i];
//coinCount가 1개 이상일 경우
if (cointCount[i] >= 1) {
//남은 잔액을 계산후 반복
total=total%arr[i];
//현재 카운트 된 동전의 금액 : 갯수
result[i][0] = arr[i];
result[i][1] = cointCount[i];
} //end if
}
}
return result;
}
output
----- coin type :
[10, 100, 50, 500]
----- after coin sort :
[500, 100, 50, 10]
----- amount : 4830
[500 : 9, 100 : 3, 0 : 0, 10 : 3]
----- amount : 11670
[500 : 23, 100 : 1, 50 : 1, 10 : 2]
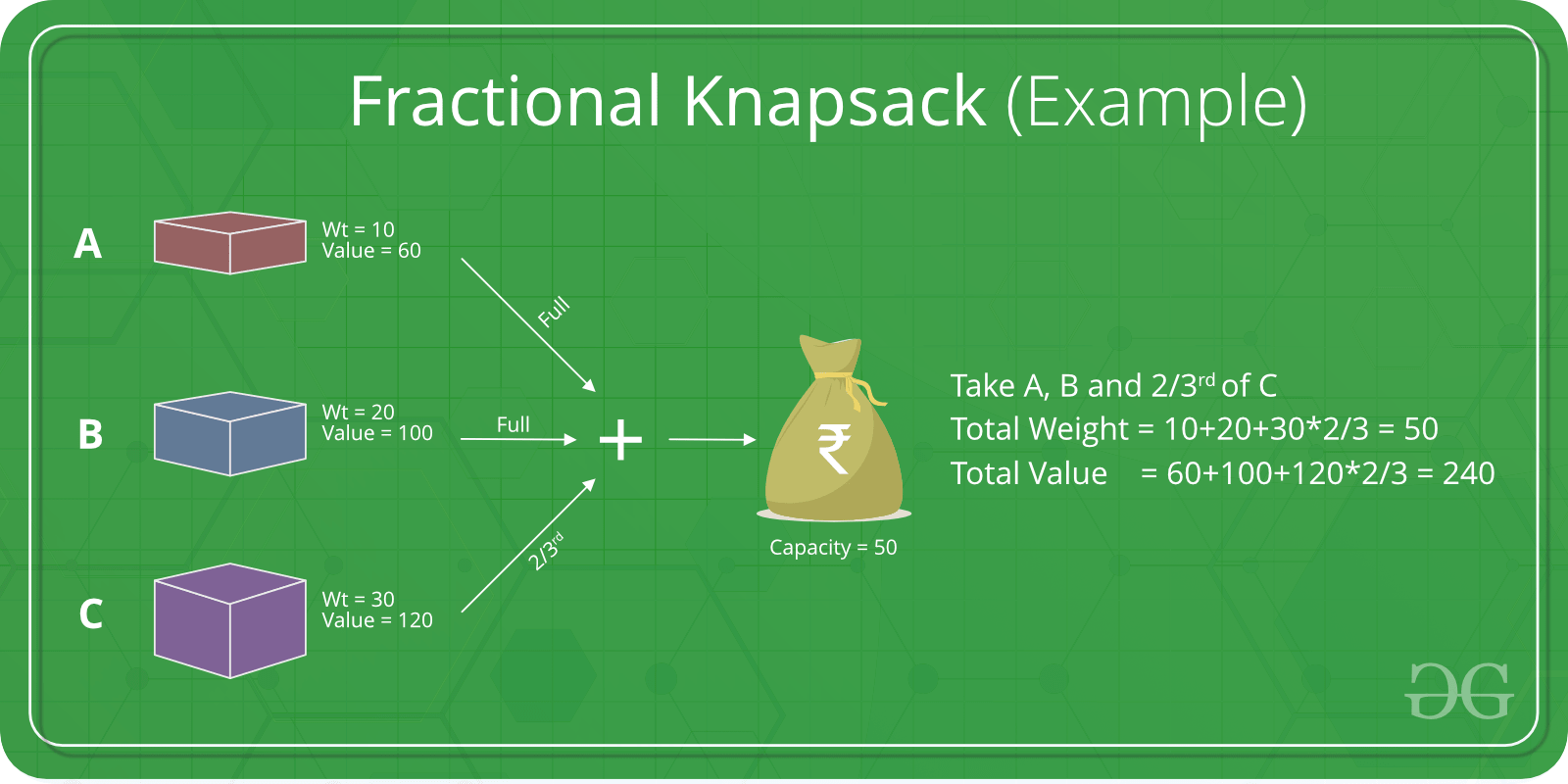
자바를 이용하여 탐욕알고리즘 - Fractional Knapsack Problem 부분 배낭 문제 구현
- 배낭이 담을 수 있는 총 capacity에 딱 맞게 아이템을 담는 문제
- 각 아이템의 무게 weight, 가치 value가 주어짐
- cost = value/weight 로 계산해서 각 아이템의 가치를 측정
- 가치가 높은 아이템 부터 담기
- 아이템 한개를 온전히 담을 수 없을때까지 까지 반복
- 아이템을 한개를 온전히 담을 수 없을땐 쪼개서 capacity채우기
private static double getMaxValue(int[] weight, int[] value, int capacity) {
ItemValue[] itemValue = new ItemValue[weight.length];
//cost계산
for (int i = 0; i < itemValue.length; i++) {
itemValue[i] = new ItemValue(weight[i], value[i], i);
}
// cost를 기준으로 내림차순 정렬
Arrays.sort(itemValue, new Comparator<ItemValue>() {
@Override
public int compare(ItemValue o1, ItemValue o2) {
return o2.getCost().compareTo(o1.getCost());
}
});
System.out.println(toString(itemValue));
double totalValue = 0d;
//cost 가 높은것부터 아이템 한개씩 꺼내서 계산
for (ItemValue item : itemValue) {
int currentWeigth = (int)item.weight;
int currentValue = (int)item.value;
//capacity가 아이템 한개를 다 담을 수 있을 때
if( capacity - currentWeigth >= 0) {
capacity = capacity - currentWeigth;
totalValue = totalValue + currentValue;
System.out.println("total value : " + totalValue + ", current weight : " +currentWeigth + ", current value : " + currentValue);
} else {
//아이템 한 개 를 다 담지 못하는 경우 쪼깸
// 남은 용량/현재 무게
double fraction = (double)capacity/(double)currentWeigth;
capacity = (int)(capacity - (currentWeigth*fraction));
totalValue = totalValue + (currentValue * fraction);
System.out.println("total value : " + totalValue + ", current weight : " +currentWeigth + ", current value : " + currentValue + ", fraction :" + fraction);
break;
}
}
return totalValue;
}
static class ItemValue{
private double weight, value, index;
private double cost;
public ItemValue(int weight, int value, int index) {
this.weight = weight;
this.value = value;
this.index = index;
//cost 계산
cost = (value/weight);
}
public double getWeight() {
return weight;
}
public double getValue() {
return value;
}
public double getIndex() {
return index;
}
public Double getCost() {
return cost;
}
}
output
[ * FractionalKnapSack * ]
capacity :50
[index : 0, cost : 6.0, value : 60, weight : 10/ index : 2, cost : 5.0, value : 100, weight : 20/ index : 3, cost : 4.0, value : 120, weight : 30/ index : 1, cost : 1.0, value : 40, weight : 40]
total value : 60.0, current weight : 10, current value : 60
total value : 160.0, current weight : 20, current value : 100
total value : 240.0, current weight : 30, current value : 120, fraction :0.6666666666666666
Maximum value = 240.0
references
https://www.javatpoint.com/greedy-algorithms
https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/greedy-algorithms/
https://www.tutorialspoint.com/data_structures_algorithms/greedy_algorithms.htm