[JAVA] 추상화(abstract) VS 인터페이스(interface)
추상화(abstract) VS 인터페이스(interface)
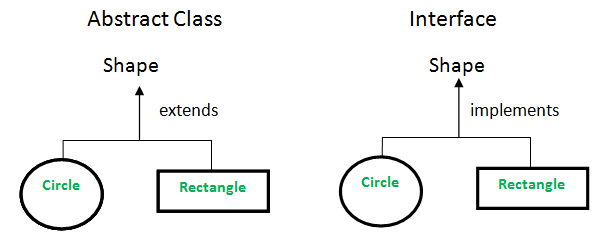
상속과 추상화
- 추상 클래스 확장은 키워드 extends를 사용
- 인터페이스 확장은 키워드 implements을 사용
메소드 유형
- 추상 클래스는 abstract 및 non-abstract methods를 가질 수 있음
- 인터페이스는 abstract methods 만 가질 수 있음. (Java 8부터는 default 및 static methods도 가질 수 있음)
- 모든 메서드가 추상 메서드인 추상클래스는 인터페이스로 변경 가능
final 변수
- 추상 클래스에는 final이 아닌 변수가 포함될 수 있음
- 인터페이스에서 선언 된 변수는 기본적으로 final (자동으로 final static 이 붙어 상수가 됨)
변수 유형
- 추상 클래스는 final, non-final, static, non-static 를 가질 수 있음
- 인터페이스에는 static 변수, final 변수 만 있음
Implementation
- 추상 클래스는 인터페이스의 Implementation 가능
- 인터페이스가 추상 클래스의 Implementation 안됨
다중 구현
- 추상 클래스는 다른 클래스를 확장하고 여러 인터페이스를 구현 가능
- 인터페이스는 다른 인터페이스만 확장
- 상속이 우선 예) A extends B implements iC
데이터 멤버의 접근성
- 추상 클래스에는 private, protected 등과 같은 클래스 멤버가능
- 인터페이스 멤버는 기본적으로 public
//Creating interface that has 4 methods
interface A{
void a();//bydefault, public and abstract
void b();
void c();
void d();
}
//Creating abstract class that provides the implementation of one method of A interface
abstract class B implements A{
public void c(){
System.out.println("I am C");
}
}
//Creating subclass of abstract class, now we need to provide the implementation of rest of the methods
class M extends B{
public void a(){System.out.println("I am a");}
public void b(){System.out.println("I am b");}
public void d(){System.out.println("I am d");}
}
//Creating a test class that calls the methods of A interface
class Test5{
public static void main(String args[]){
A a=new M();
a.a();
a.b();
a.c();
a.d();
}
}
output
I am a
I am b
I am c
I am d
references
https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/difference-between-abstract-class-and-interface-in-java/
https://www.javatpoint.com/difference-between-abstract-class-and-interface