[JAVA] 예외처리(exception)
자바 예외처리
자바 예외처리 계층 구조
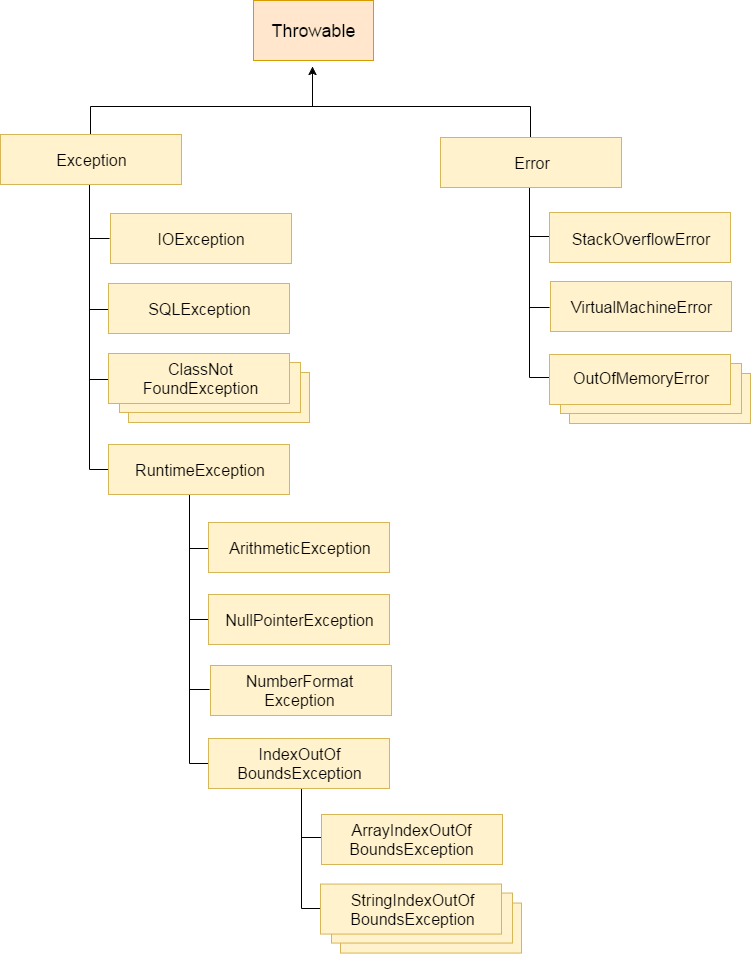
예외(Exeption) , 에러(Error)
Checked Exception
- RuntimeException 및 Error를 제외하고 Throwable 클래스를 직접 상속하는 클래스를 확인 된 예외
- 예 : IOException, SQLException
- compile-time error : 컴파일시 발생하는 에러
Unchecked Exception
- RuntimeException을 상속받는 클래스는 검사되지 않은 예외
- 예 : ArithmeticException, NullPointerException, ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException 등
- runtime error : 프로그램 실행할 때 발생하는 에러
Error
- 복구 되지 않는 에러
- OutOfMemoryError, VirtualMachineError, AssertionError
예외처리 구문
예외를 처리하려면 사용해야 함
try-catch-finally
- try : 예외 코드를 배치 할 블록을 지정하는 데 사용
- catch : 예외를 처리하는 데 사용
-
finally : 예외 처리 여부에 관계없이 실행
- 문법
try {
// Protected code
} catch (ExceptionType1 e1) {
// Catch block
} catch (ExceptionType2 e2) {
// Catch block
} catch (ExceptionType3 e3) {
// Catch block
}finally {
// The finally block always executes.
}
- 예제
public class ExcepTest {
public static void main(String args[]) {
int a[] = new int[2];
try {
System.out.println("Access element three :" + a[3]);
} catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
System.out.println("Exception thrown :" + e);
}finally {
a[0] = 6;
System.out.println("First element value: " + a[0]);
System.out.println("The finally statement is executed");
}
}
}
- output
Exception thrown :java.lang.ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException: 3
First element value: 6
The finally statement is executed
try-with-resources
- Java 7에 도입 된 새로운 예외 처리 메커니즘
- 자동 자원 관리
- try catch 블록 내에 사용 된 자원을 자동으로 닫음
- 예제1 : 괄호 안의 리소스 선언을 제외하고 모든 것은 try 블록의 일반적인 try / catch 블록과 동일
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.IOException;
public class Try_withDemo {
public static void main(String args[]) {
//try : use the resource
try(FileReader fr = new FileReader("E://file.txt")) {
char [] a = new char[50];
fr.read(a); // reads the contentto the array
for(char c : a)
System.out.print(c); // prints the characters one by one
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
- 예제2 : sql connection에서도 사용 가능
public static void viewTable(Connection con) throws SQLException {
String query = "select COF_NAME, SUP_ID, PRICE, SALES, TOTAL from COFFEES";
try (Statement stmt = con.createStatement()) {
ResultSet rs = stmt.executeQuery(query);
while (rs.next()) {
String coffeeName = rs.getString("COF_NAME");
int supplierID = rs.getInt("SUP_ID");
float price = rs.getFloat("PRICE");
int sales = rs.getInt("SALES");
int total = rs.getInt("TOTAL");
System.out.println(coffeeName + ", " + supplierID + ", " +
price + ", " + sales + ", " + total);
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
JDBCTutorialUtilities.printSQLException(e);
}
}
throws-throw
- throws : 예외를 선언하는 데 사용되나, 예외는 발생하지 않음. 메소드에 예외가 발생할 수 있음을 지정. 항상 메소드 서명과 함께 사용
- throw : 예외를 발생시키는 데 사용됨 (새로 인스턴스화 된 예외 또는 방금 포착 한 예외를 예외로 처리)
- throws 는 확인 된 예외 처리를 연기하는 데 사용 되며 throw 는 명시 적으로 예외를 호출하는 데 사용
import java.io.*;
public class className {
// RemoteException을 던진다는 것을 선언
public void deposit(double amount) throws RemoteException {
// Method implementation
// RemoteException 예외 처리
throw new RemoteException();
}
// Remainder of class definition
}
references
https://www.tutorialspoint.com/java/java_exceptions
https://www.javatpoint.com/exception-handling-in-java
https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/exceptions-in-java/?ref=lbp
https://docs.oracle.com/javase/tutorial/essential/exceptions/tryResourceClose.html