[JAVA] Collection Framework (List, Set, Map)
JCF : Java Collections Framework (List, Set, Map)
The Collection framework represents a unified architecture for storing and manipulating a group of objects. It has:
- Interfaces and its implementations, i.e., classes
- Algorithm
- 배열을 사용하지 않고 여러개의 문자열 입력
- 자료구조 방법인 Set, List, Map이 핵심
- The Collection interface (java.util.Collection) & Map interface (java.util.Map)
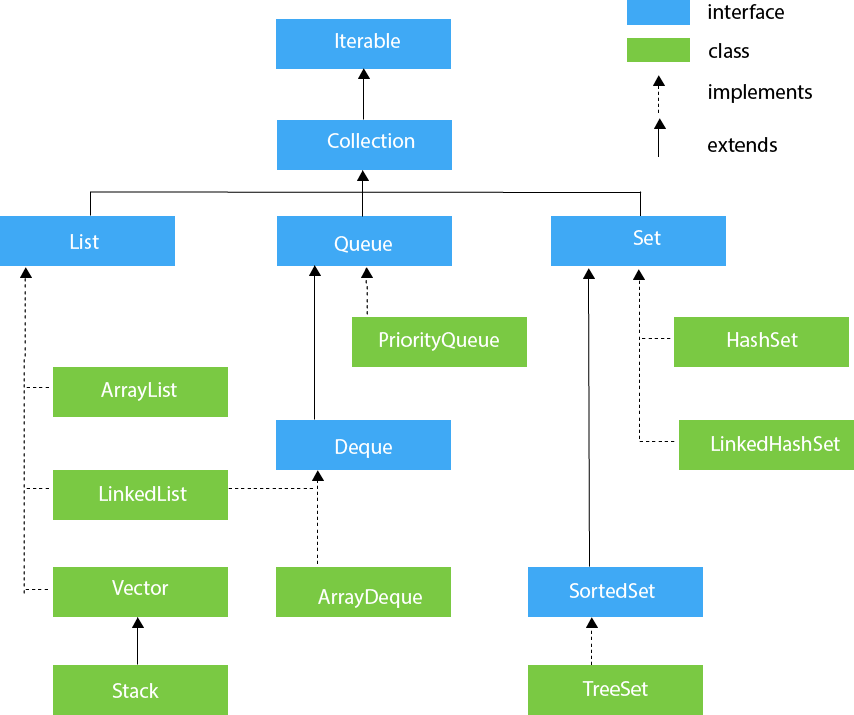
List
- 순서 있고 중복 허용
- ArrayList, LinkedList, Vector, Stack
List <data-type> list1= new ArrayList();
List <data-type> list2 = new LinkedList();
List <data-type> list3 = new Vector();
List <data-type> list4 = new Stack();
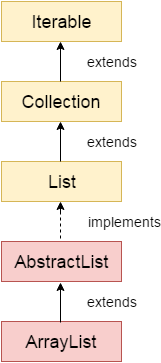
ArrayList
- non-synchronization : 별도의 동기화처리 필요
- 데이터를 읽어오는데 걸리는 시간이 가장 빠름
- 크기 변경 어려움
- 추가, 삭제시 데이터의 많은 이동이 필요하므로 LinkedList보다 조작 속도가 약간 느림
ArrayList<String> list=new ArrayList<String>();//Creating arraylist
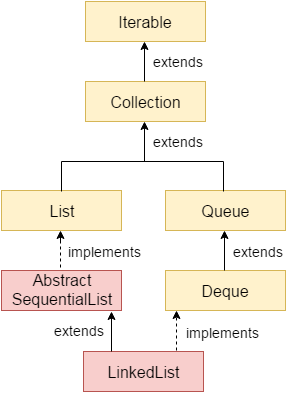
LinkedList
- non-synchronization : 별도의 동기화처리 필요
- array의 단점을 보완
- 추가, 삭제시 데이터의 이동이 필요없기 때문에 조작이 빠름
- 불연속적으로 존재하는 데이터를 연결
- doubly linked list (이중연결 리스트)
- doubly circular linked list (이중 원형 연결 리스트)
LinkedList<String> al=new LinkedList<String>();
Vector
- synchronization : 자체적으로 동기화처리 되어 짐
- ArrayList와 비슷 (array list가 vector를 개선한 것)
Vector<String> v=new Vector<String>();
Stack
- Vector의 subclass
- LIFO( last-in-first-out ) data structure
Stack<String> stack = new Stack<String>();
Set
- 순서 없고 중복 안됨
Set<data-type> s1 = new HashSet<data-type>();
Set<data-type> s2 = new LinkedHashSet<data-type>();
Set<data-type> s3 = new TreeSet<data-type>();
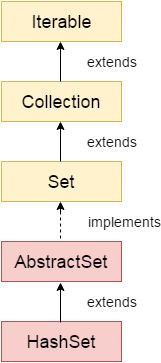
HashSet
- 해싱(hashing) 이라는 메커니즘을 사용하여 요소를 저장
- null 값을 허용
- non-synchronization
- 검색 작업에 가장 적합한 방법
- 순서를 유지하고 싶다면 LinkedHashSet 사용
- hashCode() : 해쉬코드값 반환
- equals() : 객체의 hashCode()값 비교
HashSet<String> set=new HashSet<String>();
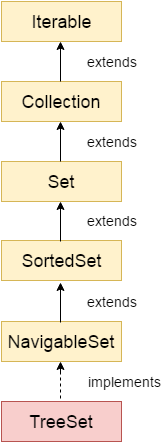
TreeSet
- 검색과 정렬에 유리 (정렬 저장)
- binary search tree (이진검색트리) 구조로 되어있음
- linked list와 같이 node가 tree 형태로 연결된 구조
- hashSet보다 데이터 추가, 삭제 시간이 더 걸림
- non-synchronization
- null 키를 가질 수 없지만 여러 null 값은 허용
TreeSet<String> set=new TreeSet<String>();
Map
- key, value가 한 쌍
- key는 중복 안됨. value는 중복 허용

HashMap
- HashMap <K, V>
- non-synchronization
- 하나의 null key 와 여러 개의 null value 허용
HashMap<Integer,String> map=new HashMap<Integer,String>(); //Generic
TreeMap
- binary search tree (이진검색트리) 구조로 되어있음
- map의 장점인 빠른 검색 + tree의 장점인 정렬과 범위 검색 장점을 모두 가짐
- 저장할때, 정렬하기 때문에 저장시간이 길어짐
- 정렬이나 범위검색이 필요한 경우에 사용
TreeMap<Integer,String> map=new TreeMap<Integer,String>();
references
https://www.javatpoint.com/collections-in-java
https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/collections-in-java-2/?ref=lbp